There are thousands of different cryptocurrencies on the market, but not many of them provide users with real utility — or find their footing and rise to the top despite direct competition with other top crypto coins and tokens. Avalanche, however, is one of such crypto assets. But what is AVAX, and how does it work? Let’s take a look at one of Ethereum’s most successful competitors.
What Is AVAX Crypto?

AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche platform, a blockchain network that aims to offer high throughput, low latency, and unparalleled scalability. Unlike many of its predecessors, Avalanche distinguishes itself with a unique architecture designed to solve some of the blockchain trilemma’s most significant challenges: security, scalability, and decentralization.
Avalanche positions itself as a direct competitor to Ethereum, seeking to address some of the scalability and transaction speed issues that have plagued the latter. AVAX serves multiple purposes within the Avalanche ecosystem. It is used to pay transaction fees, secure the network through staking, and act as a basic unit of account across multiple blockchains within the Avalanche network.
One of the key features of Avalanche is its consensus mechanism, which is a novel approach combining the benefits of both classical consensus and Nakamoto consensus mechanisms. This facilitates rapid transaction processing (reportedly thousands per second) without sacrificing network security. Moreover, the Avalanche network supports the creation of Subnets, essentially allowing for the creation of custom, application-specific blockchains that can operate under their own rules while still benefiting from the security and interoperability of the main Avalanche network.
A Subnet is a sovereign network that has its own set of rules guiding token economics and membership. This set of nodes/validators is responsible for reaching a consensus for transactions on one or multiple blockchains.
Who Created Avalanche?
Avalanche was created by a team of researchers, computer scientists, and experts in various fields, led by Emin Gün Sirer. Sirer is a well-known figure in the computer science and cryptocurrency communities, with a rich background in peer-to-peer systems, distributed computing, and blockchain technology. He is a professor at Cornell University, where his research has focused extensively on the scalability and security aspects of blockchain technologies.
The project originated from a whitepaper published in 2018, titled “Snowflake to Avalanche: A Novel Metastable Consensus Protocol Family for Cryptocurrencies.” The paper introduced a new family of consensus protocols that promised significant improvements over existing blockchain systems. Following the publication, Sirer co-founded Ava Labs with Kevin Sekniqi and Maofan “Ted” Yin, Ph.D. candidates from Cornell University, to develop and implement the ideas presented in the whitepaper into what would become the Avalanche platform.
How Does Avalanche Work?
Avalanche (AVAX) operates on an innovative platform designed to address the longstanding challenges faced by blockchain technology: scalability, security, and decentralization. At its core, Avalanche introduces a novel approach to consensus that enables the network to achieve remarkable throughput and near-instant finality, setting it apart from traditional blockchains.
Avalanche’s unique consensus mechanism blends classical consensus and Nakamoto consensus models. Unlike the proof-of-work (PoW) model used by Bitcoin, which relies on a single chain of blocks, Avalanche utilizes a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure for transactions alongside multiple chains within its ecosystem. This setup allows for parallel processing, significantly increasing the network’s capacity and transaction speed.
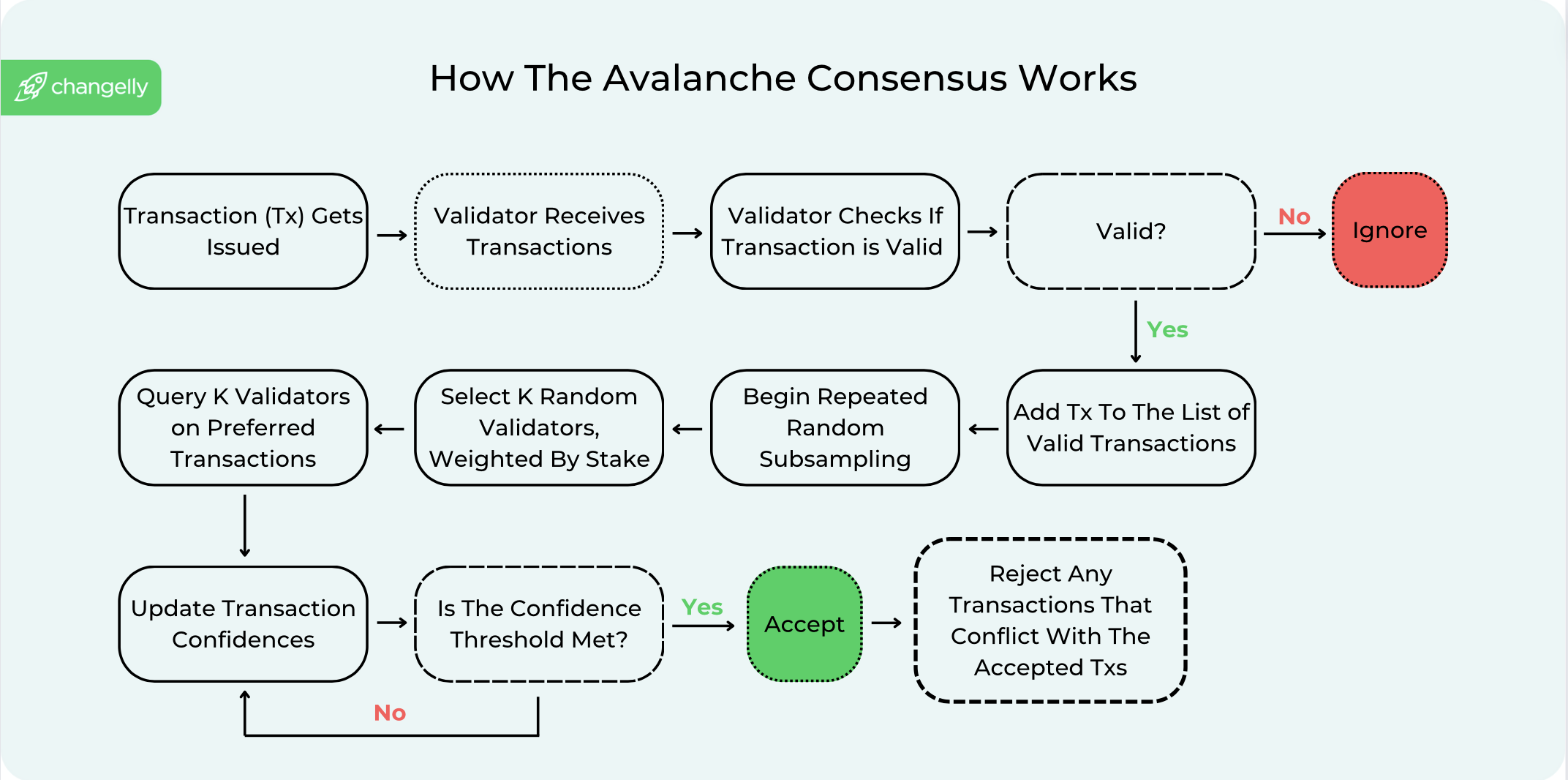
Avalanche consensus operates on the principles of sub-sampled voting. Instead of requiring the entire network to validate a transaction, it randomly selects a subset of validators to reach a decision quickly. This process repeats across several rounds, with each round achieving a higher confidence level in the transaction’s validity until it becomes practically irreversible. This method allows Avalanche to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), with transaction finality achieved in under two seconds, a significant improvement over networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Network Structure
The Avalanche network is composed of three individual blockchains, each serving a distinct purpose:
- X-Chain (Exchange Chain): This chain is responsible for creating and trading AVAX tokens and other digital assets. It uses the Avalanche consensus mechanism.
- C-Chain (Contract Chain): The C-Chain enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), making it easy for developers to migrate their projects from Ethereum to Avalanche.
- P-Chain (Platform Chain): This chain coordinates validators, tracks active Subnets, and allows for the creation of new custom Subnets. It employs the Snowman consensus protocol, a variant of Avalanche consensus optimized for smart contracts and simple transaction sequences.
The Role of AVAX
AVAX is a native cryptocurrency of the Avalanche network; it plays several critical roles within its ecosystem. Firstly, it’s used to pay transaction fees on the network, incentivizing validators to process transactions. Secondly, AVAX is used for staking, where validators lock up a certain amount of tokens as collateral to participate in the consensus process, thus securing the network. The staking mechanism also ensures a degree of decentralization, as anyone with enough AVAX can become a validator. Thirdly, it is a requirement to participate in Avalanche network governance: only AVAX owners can vote for changes in the ecosystem. Last but not least, one of its other major use cases is providing a basic unit of account between different Subnets on Avalanche.
The token has a maximum supply of 720 million, with mechanisms in place to control inflation and encourage scarcity, influencing its value proposition.
Avalanche vs. Ethereum
Avalanche and Ethereum are both prominent names in the blockchain industry, each serving as a foundational blockchain platform with distinct characteristics yet sharing some fundamental similarities. Ethereum, the first blockchain ecosystem to support decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, has established itself as the primary network for developers seeking a smart contracts platform. Its ability to support ERC-20 tokens has made it a preferred medium of exchange and investment within the crypto community.
Avalanche is Ethereum’s competitor, offering a unique consensus mechanism that emphasizes scalability and near-instant transaction finality. This feature particularly appeals to users and developers frustrated by Ethereum’s scalability issues and longer transaction times.
Ethereum’s long-standing position in the market has given it a huge catalog of dApps and ERC-20 tokens, making it a cornerstone of the blockchain industry. Avalanche, while newer, distinguishes itself by offering lower transaction fees and faster processing times, addressing some of the scalability concerns associated with Ethereum. Both networks have taken significant steps towards interoperability and sustainability, aiming to reduce their environmental impact and improve user experience.
FAQ
How can I buy AVAX?
You can buy AVAX with fiat on most major crypto exchanges. If you are looking for a reliable cryptocurrency exchange, you can check out our platform.
Is the Avalanche blockchain safe?
The Avalanche blockchain is regarded as safe, utilizing advanced cryptography and consensus mechanisms to protect against attacks. Its compatibility with hardware wallets offers Avalanche users an added layer of security for their assets, ensuring that even in the volatile cryptocurrency market, funds remain secure within a user’s chosen crypto wallet.
What makes Avalanche unique?
What makes Avalanche unique is its revolutionary consensus protocol, designed for rapid transaction processing and scalability without compromising decentralization. This distinctive feature attracts developers looking for a robust blockchain project foundation, enabling a wide range of applications from decentralized finance to digital collectibles, all while maintaining near-instant transaction finality.
What is AVAX used for?
AVAX is used primarily as the native token within the Avalanche ecosystem, facilitating various transactions and operations. It serves as a medium of exchange for paying transaction fees, a staking token for securing the network, and a basic unit of account for the multiple subnets, making it a versatile asset in the crypto wallet of Avalanche users and participants in the broader cryptocurrency market.
Is AVAX a good investment?
Avalanche is one of the biggest tokens on the cryptocurrency market. At the time of writing, its market cap was within the top 10 on CoinMarketCap. Additionally, it has a solid technical foundation, a reputable team behind it, and a variety of use cases. Overall, AVAX can be a good investment — but you should do your own research before buying Avalanche and see if it fits your portfolio.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.


