The evolution of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has brought some of the most innovative solutions for financial services, both on- and off-chain. Lending, trading, staking, and tokenization are just some of the most popular DeFi trends that have accumulated billions of dollars in total value locked (TVL).
In 2024, DeFi is seeing several emerging trends that are transforming the landscape. They are reshaping the ecosystem by enhancing liquidity, security, and scalability, driving broader adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) and new financial tools.
This article will guide you through some of the hottest DeFi trends in 2024. As always, let’s start with the basics: the definition of DeFi and its core principles.
Quick Navigation
- What is DeFi
- Top DeFi Trends in 2024
- Liquid Staking: Maximizing Yield and Maintaining Network Security
- Top Liquid Staking and Restaking Projects
- Lido Finance
- EigenLayer
- Solayer
- Jito Restaking
- Top Liquid Staking and Restaking Projects
- Real-World Assets and Bond Tokenization (RWA)
- Types of RWA Protocols
- Top RWA Projects
- The Rise of Layer-1s
- The Rise of Layer-2s
- Top Layer-1 and Layer-2 Chains
- Aptos
- Sui Network
- Base
- Arbitrum
- Optimism
- Cross-Chain Bridges
- Top Cross-Chain Bridges
- Stargate Finance
- Across Protocol
- Synapse Protocol
- Top Cross-Chain Bridges
- The Rise of Prediction Markets
- Closing Thoughts: The Top DeFi Trends in 2024

What Is DeFi?
DeFi refers to a financial ecosystem consisting of decentralized applications (dApps) built on blockchain networks, especially Ethereum. While there’s no exact date marking the start of DeFi, its emergence is attributed to the gradual development of blockchain components and innovations addressing various financial challenges.
DeFi operates on decentralized blockchain networks, meaning no single entity controls the system, unlike traditional finance, where institutions manage transactions. Instead, DeFi relies on smart contracts—self-executing agreements triggered by specific conditions.
DeFi offers a variety of financial services—lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest—without the need for intermediaries. If you’re interested, check out some of the best DeFi projects that are currently dominating the market.
Some of DeFi’s core principles are:
- Decentralization: Direct user-to-user transactions, no intermediaries or middlemen.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public blockchain, making them verifiable and auditable. However, you might see permissioned (private) blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric and permissionless (public) blockchains like Ethereum.
- Inclusivity: DeFi is (mostly) accessible to anyone, regardless of geographic location or financial status. This is especially important for unbanked populations or where access to international transfers is complicated.
- Programmability: Smart contracts automate processes like transactions and data storing and enable the development of new financial products.
What about control and decision-making? Well, DeFi projects are often governed by decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which establish governance structures that may include voting mechanisms and protocol development.
Top DeFi Trends in 2024
Ok, now that the basics are out of the way, dive into this guide to explore some of the top DeFi trends in 2024. The following trends do not have a proper order.
Liquid Staking – Maximizing Yield and Maintaining Network Security
Liquid staking has emerged as a key innovation within DeFi, offering you the flexibility to manage your staked assets across other dApps.
The idea is simple—you deposit your crypto assets into a liquid staking protocol, which then stakes the assets on your behalf. In return, you receive tokenized versions of your assets, acting as representations of your staked funds.
The appeal of liquid staking lies in the ability to maintain liquidity while earning rewards. You can use these tokenized assets in various ways, such as posting them as collateral in lending protocols, trading on decentralized exchanges, or even restaking them on other platforms for additional rewards.
With the evolution of liquid staking, restaking soon emerged as the new game-changer. As the name suggests, involves staking already staked tokens. It was an answer to the limitations of traditional staking mechanisms.
Restaking became one of the hottest DeFi trends in mid-2023—and still is today—thanks to protocols like EigenLayer. The concept of a mechanism that could boost yields for stakers but also heighten the security of blockchain protocols opened new opportunities in the Ethereum ecosystem for both DeFi developers, crypto projects, and ETH stakers.
Top Liquid Staking and Restaking Projects
Lido Finance
Lido is the leading liquid staking protocol. This protocol has been so successful in the sector that it reached a TVL of nearly $40 billion in early 2024.
It’s the largest decentralized liquid staking protocol. It allows you to stake ETH while receiving a liquid staked token called stETH, which is a representation of your already staked ETH which you can use through other dApps on the Ethereum ecosystem.
EigenLayer
EigenLayer is a decentralized protocol on Ethereum that introduces the concept of restaking, where users deposit staked Ethereum (stETH) or liquid staked tokens (LSTs) into the protocol’s liquidity pools. These tokens are then restaked across various decentralized protocols on Ethereum, referred to as Actively Validated Services (AVS).
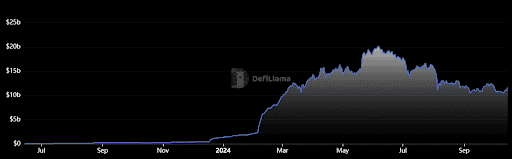
AVS includes a wide range of services, such as oracles, sidechains, Layer-2 networks, data availability layers, and cross-chain bridges—essentially any system that relies on distributed validation to secure its network. EigenLayer acts as the middleware, distributing staked tokens across different DeFi protocols, enhancing their mainnets’ security.
Ethereum is not the only blockchain with restaking protocols (other restaking solutions are Symbiotic and Karakc, both exceeding one billion USD in TVL). Several players in the Solana network have decided to capitalize on the emerging trend of restaking assets.
Solayer
Solayer is a restaking protocol on the Solana blockchain, co-founded by Rachel Chu and Jason Li. It allows you to restake their SOL tokens or liquid staking tokens (LSTs) to secure bandwidth for dApps, enhancing performance and earning additional rewards.
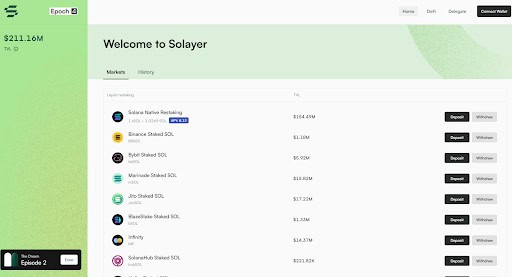
By converting staked SOL into sSOL, you can leverage liquidity across integrated platforms and earn yield through validator returns and restaking incentives. Since its soft launch in May 2024, Solayer has gained significant traction, climbing the Solana leaderboard and becoming the top Solana projects with over $200M in TVL.
Jito Restaking
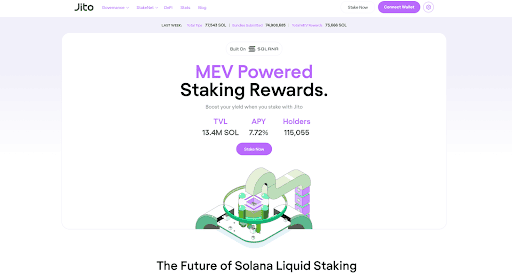
Jito, which is the largest liquid staking protocol on Solana, is also stepping up its game with a restaking mechanism (still in the works as of October 2024). We’re talking about Jito (re)staking, a hybrid system that includes two key components: the Vault Program and the Restaking Program.
The Vault Program manages the creation and delegation of Liquid Restaking Tokens (VRTs) using any SPL token as the underlying asset. It allows for flexible delegation strategies, customized slashing conditions, and supports governance via DAOs or on-chain automation tools like StakeNet.
The Restaking Program focuses on managing Node Consensus Operators (NCNs) and operators, handling reward distribution, and enforcing slashing penalties, providing a robust framework for economic security.
Real-World Assets and Bond Tokenization
Real-world assets (RWAs) are digital tokens representing physical or financial assets, such as real estate, commodities, bonds, equities, artwork, and intellectual property. This is thanks to tokenization—the process of bringing these off-chain assets onto the blockchain, using cryptography to replace sensitive information with non-sensitive data and create a token.
Tokenization allows traditionally illiquid assets to be divided into smaller, accessible units, enhancing liquidity and broadening market participation. This method has become particularly attractive for US treasuries, which are now a $2.27B market, with key leaders like BlackRock’s BUIDL and Ondo Finance’s USDY both reaching over $500M in deposited value.
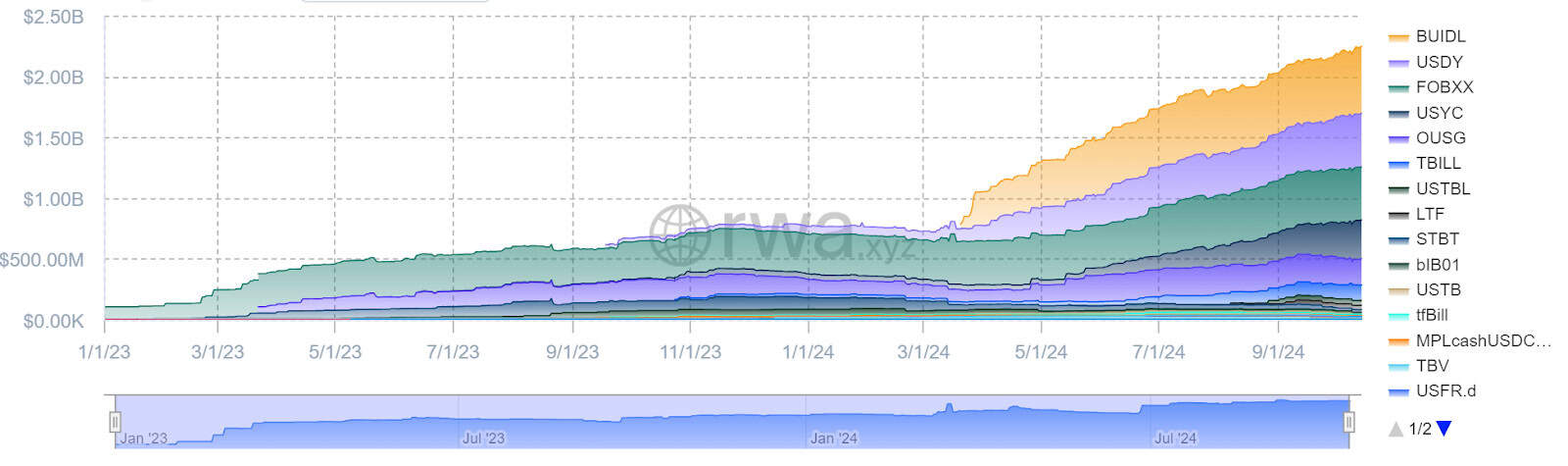
Types of RWA Protocols
The RWA market is extensive, and it incorporates a varied list of protocols addressing issues across multiple industries, but the main (hottest) fields in RWA are:
- Public Credit/Equities (US Treasuries): These protocols tokenize financial assets like stocks and bonds. Ondo Finance and Backed Finance, for instance, offer tokenized US Treasuries and fixed-income products.
- Real Estate: Platforms like Tangible tokenize real estate, enabling users to mint stablecoins backed by real estate and even offer fractional ownership through NFTs, increasing liquidity and lowering entry barriers.
- Debt/Private Credit: Protocols such as MakerDAO and Centrifuge focus on tokenizing loans and debt instruments, offering innovative solutions for real-world lending.
- Climate/Carbon Credits: These protocols, like those tokenizing carbon credits, facilitate efficient trading and offsetting of carbon footprints, helping businesses manage climate-related financial instruments.
- Precious Metals/Commodities: Pax Gold, for example, tokenizes commodities like gold, enabling fractional ownership and easier trading of traditionally cumbersome assets.
Why are RWAs and tokenization one of the hottest DeFi trends? Well, they offer new financial opportunities by bridging the gap between traditional finance and blockchain, enabling assets to serve as collateral, be included in index funds, be managed autonomously, and other perks.
This integration has the potential to create more inclusive financial systems, bringing traditional investment products to the blockchain with the added benefits of transparency, security, and efficiency.
Top RWA Projects
Ondo Finance
Ondo Finance, the largest real-world asset (RWA) protocol in 2024, offers institutional-grade financial products by tokenizing stable, yield-generating assets from traditional finance, such as treasury bonds.

Ondo enhances the accessibility of RWAs by integrating these tokenized products across multiple blockchain networks like Ethereum, Aptos, and Solana. USDY, its flagship product, is one of the largest yield-bearing stablecoins.
Founded by Nathan Allman in 2021, Ondo Finance has attracted significant investment, raising over $34 million from investors such as Wintermute, Founders Fund, and Pantera Capital. The protocol also runs KYC checks to ensure regulatory compliance. Governed through the Ondo Foundation and Ondo DAO, the platform blends the reliability of traditional finance with the transparency and efficiency of blockchain technology.
Centrifuge
Centrifuge is one of the largest real-world asset (RWA) protocols, focused on reducing capital costs for small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) while providing investors with stable income.
Centrifuge integrates physical assets into the DeFi space, enhancing collateral transparency and offering diversified, stable yields. The platform allows businesses to use these assets as collateral for financing by tokenizing assets such as invoices, real estate, and royalties.
Notably, Centrifuge has secured partnerships with leading DeFi platforms, like MakerDAO (now rebranded to Sky). It has also raised over $30M in a Series A funding round.
The Rise of Layer-1s
The rise of layer-1s like Aptos and Sui reflects a growing trend towards alternative blockchains that can offer a balanced degree of scalability, security, and a developer-friendly environment.
These two blockchains are at the forefront of the layer-1 game. Both platforms leverage the Move programming language—which is considered one of the best alternatives to the Ethereum Virtual Machine—but differ in their architecture and consensus mechanisms. Aptos focuses on a modular structure and BFT consensus, while Sui implements a DAG-based architecture with a unique asynchronous protocol.
These innovations aim to address the limitations of earlier blockchains like Ethereum and cater to the growing demand for efficient dApps across various industries, including gaming, finance, and social networking.
The Rise of Layer-2s
Layer-2 scaling solutions are chains connected to a mainnet (a layer-1 like Ethereum). They are designed to improve the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks by processing transactions faster and at lower costs—without compromising the security and decentralization of the underlying network.
There are several types of Layer-2 solutions, including State Channels, which allow you to conduct multiple transactions off-chain, with only the final transaction state recorded on the main blockchain; sidechains like Polygon, an Independent blockchain that runs parallel to Ethereum; and rollups, the most popular types of blockchain scaling solutions.
Rollups bundle multiple transactions into a single batch before submitting them to the main chain. There are two main types of rollups:
- Optimistic Rollups: Assume transactions are valid and only check them if a dispute arises.
- Zero-Knowledge Rollups (zk-Rollups): Use cryptographic proofs to validate transactions off-chain before submitting them to the main chain.
Layer-2 solutions are some of the most popular DeFi trends in 2024. Data from L2Beat shows the total value locked across layer-2s has increased 232% in one year, currently boasting over $37B.
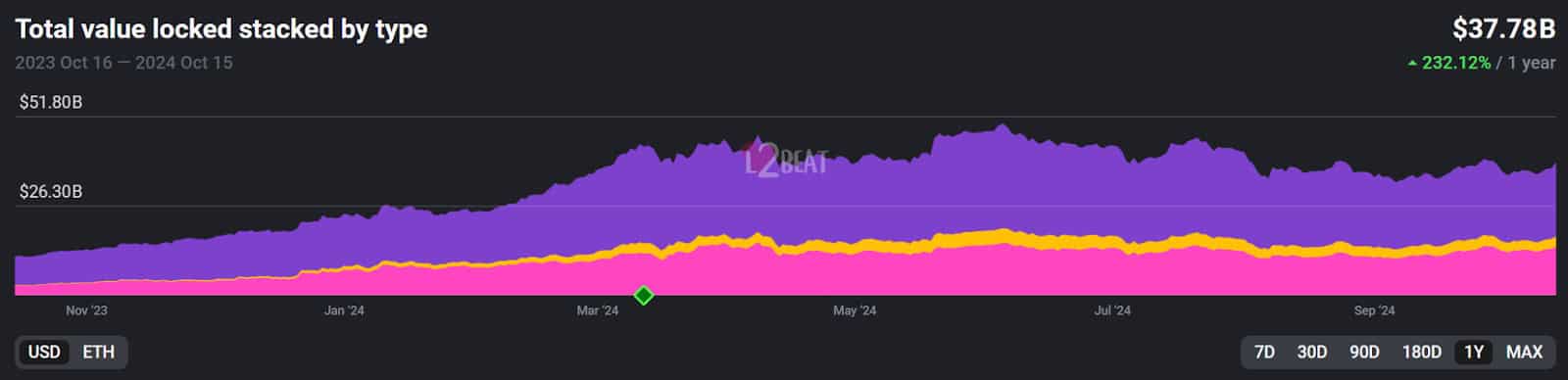
Today, we have layer-2s left and right. Centralized exchanges like Coinbase launched Base in 2023. Its decentralized counterpart, Uniswap, recently got into action, too, with the launch of Unichain, promising faster and cheaper transactions and interoperability across multiple blockchain networks.
Top Layer-1 and Layer-2 Chains
Aptos
Aptos launched its mainnet in October 2022 after three years of development, raising around $350 million in venture capital. It positions itself as a high-performance blockchain, often compared to Solana due to its focus on scalability and reliability. In the Aptos community, the network is often called the Solana killer.
One thing that stands out about Aptos is its use of complex technology. First, it uses Move due to its emphasis on security and flexibility—particularly in smart contract development. Second, it uses a Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) variant of Proof of Stake (PoS) to provide high security and fast transaction confirmations.
Moving on, the Aptos blockchain has a modular architecture that divides various components of the network—consensus mechanism, data storage, transaction execution, etc.—into separate modules, providing faster development cycles, faster improvements, and higher scalability.
As it weren’t enough, Aptos’ Block-STM technology enables parallel transaction processing, with claims of handling up to 160,000 transactions per second (TPS). The platform also aims to implement sharding to improve scalability by allowing multiple ledger states to interact through standardized bridges.
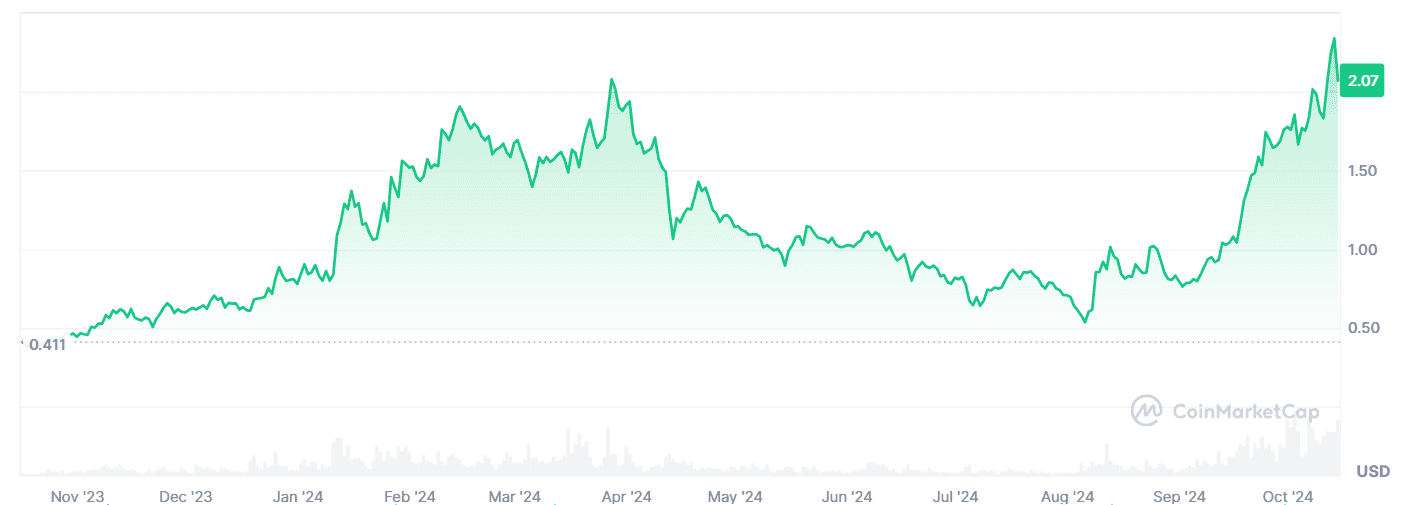
Its native coin, APT, has surged over 113% in the yearly chart, reflecting the protocol’s growing interest and network activity.
Sui Network
Sui Network is a layer-1 launched in 2023, focusing on simplifying the creation and deployment of dApps and become an alternative development environment for crypto projects.
Like Aptos, Sui uses the Move programming language, but it takes an object-centric approach, allowing developers to define assets with strict ownership rules, improving the security of dApps built on the platform.
Sui’s consensus mechanism is also different from Aptos, as it uses Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) combined with an asynchronous protocol called Narwhal and Bullshark. This setup supports parallel transaction processing, boosting the network’s efficiency and scalability.
Further, Sui’s architecture is based on a directed acyclic graph (DAG), enabling more efficient transaction processing than traditional blockchain structures. This design allows for concurrent execution of multiple transactions, providing high throughput and low latency for dApps.
SUI, Sui’s native coin, is one of the best-performing crypto assets in 2024, having surged almost 400% on the yearly chart.
Base
Base is a Layer-2 scaling solution built on Ethereum, developed by Coinbase in collaboration with Optimism.

Officially launched on August 9, 2023, Base was created using the OP Stack and is designed to improve Ethereum’s scalability, speed, and cost-efficiency while preserving its security and decentralization.
Base processes transactions off-chain, significantly increasing its transaction capacity compared to Ethereum Layer 1. This higher throughput helps ease network congestion, ensuring faster transaction processing by reducing the computational load on the main chain. It also leads to lower transaction fees, making it a more affordable option than transacting directly on Ethereum.
If you’re interested, check out our picks for the best Base wallets in 2024.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is the leading layer-2 solution, capable of processing billions of transactions in a single week.
Arbitrum processes transactions in batches off-chain and returns only essential data to Ethereum, reducing congestion while ensuring that all actions can be audited and verified when necessary.
Arbitrum consists of several components designed to enhance scalability and offer different solutions for various use cases:
- Arbitrum One is the primary rollup chain that enables developers to build scalable dApps while benefiting from Ethereum’s security.
- Arbitrum Nova is a newer chain optimized for high-throughput applications, such as gaming. It utilizes AnyTrust technology to further reduce costs.
- Arbitrum Nitro provides an advanced technical stack that improves throughput and lowers fees while maintaining full compatibility with Ethereum.
- Arbitrum Orbit allows developers to launch their own customized chains that connect to the broader Arbitrum ecosystem.
Optimism
Optimism is a Layer-2 launched in December 2021 as an answer to Ethereum’s scalability issues.
One of Optimism’s core features is its use of Optimistic Rollups, a technology that processes most transactions off-chain by bundling multiple transactions into a single batch, which is later submitted to the Ethereum mainnet for validation.
Transactions are presumed valid by default (hence the name optimistic), enabling faster processing without the need for immediate verification. However, this has its downsides. Assuming that all blocks are valid means Optimism relies on honest validators to challenge fraudulent transactions.
Optimism is also fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to port their existing decentralized applications (dApps) onto Optimism with minimal modifications. This compatibility lowers the barriers to adoption, as developers can easily transition to the platform.
Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges are becoming essential in enabling seamless asset transfers between different blockchain ecosystems.
A cross-chain bridge is pretty much what it sounds like—a protocol that facilitates the movement of digital assets between separate blockchains. It works by locking an asset on one blockchain and creating an equivalent token on another.
Say, for example, you want to bridge Ethereum (ETH) to the Solana network. In this case, the bridge locks your ETH and mints (issues) a wrapped version of it (like Wrapped Bitcoin, WBTC) on Solana. However, keep in mind this method, called lock and mint, is not the only way to do it. Some bridges use liquidity pools to facilitate swaps between tokens directly.
There are different models used by cross-chain bridges:
- Lock-and-Mint: The original asset is locked on the source chain, and a new token is minted on the target chain.
- Burn-and-Mint: A token is burned on one chain, which triggers minting on another chain.
- Lock-and-Unlock: Tokens are locked on one chain, and equivalent tokens are unlocked from a liquidity pool on the other chain.
Cross-chain bridges bring significant advantages to the blockchain space, and they have become a fundamental pillar of blockchain interoperability.
They allow seamless asset transfers between platforms by enabling different blockchains to communicate with each other, which is particularly beneficial for users, developers, projects, etc. These bridges also help increase liquidity by allowing less popular chains to tap into liquidity pools from more established networks. This leads to lower transaction fees and reduced slippage, ultimately enhancing trading opportunities.
Additionally, cross-chain bridges contribute to blockchain scalability by distributing transaction loads across various chains, which helps alleviate congestion on older networks. As new chains emerge with faster processing capabilities, these bridges allow them to be integrated into the ecosystem more easily.
Data from DeFillama shows that trading volume across all crypto bridges spiked during the first three quarters of 2024. In September, trading volume surged to $8.15B.
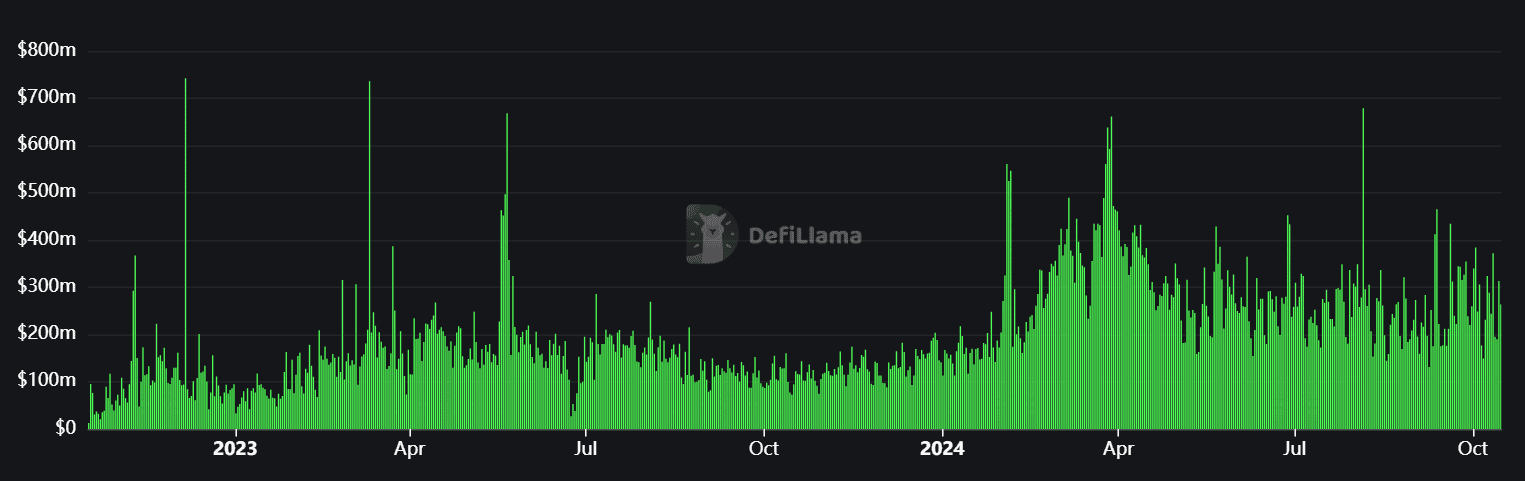
Top Cross-Chain Bridges
Stargate Finance
Stargate Finance is a popular crypto bridge powered by LayerZero technology, which facilitates direct native asset transfers between blockchains.
One of its standout features is unifying liquidity pools across different chains, boosting transaction efficiency and helping reduce slippage, making transfers more reliable and cost-effective. That’s not all—the protocol ensures instant transaction confirmation, meaning assets are guaranteed to arrive on the target chain immediately once a transaction is confirmed on the source chain. This results in a smoother, faster experience.
Additionally, Stargate employs the Delta Algorithm, which efficiently manages liquidity in the pools, preventing exhaustion during high transaction volumes. There’s no need for wrapped tokens—you can simply send native assets directly across blockchains, making cross-chain transactions simpler and more intuitive.
Across Protocol
Across focuses on optimizing cross-chain transfers by maximizing capital efficiency and security. It relies on a unified liquidity pool hosted on the Ethereum Mainnet, which enhances capital efficiency for transactions across multiple networks.
Across uses a decentralized network of competitive relayers to ensure that transactions are completed at the best speed and cost. These relayers compete to fulfill user intents, ensuring that your transactions are executed efficiently.
UMA’s Optimistic Oracle bolsters the bridge’s security by creating a secure environment for cross-chain transfers while maintaining high speeds and low transaction costs.
Synapse Protocol
Synapse Protocol is a versatile cross-chain bridge that supports both EVM and non-EVM blockchains. It offers canonical token bridging, which allows users to bridge wrapped assets between chains efficiently. For native assets, Synapse employs liquidity-based bridging, using cross-chain stable swap pools to facilitate reliable asset transfers.
Synapse also offers robust developer tools, providing APIs that enable developers to integrate cross-chain functionality into their decentralized applications. This flexibility fosters innovation in DeFi solutions, allowing developers to build more interconnected dApps. With nearly $14 billion in total transaction volume, Synapse has established itself as a trusted platform for cross-chain bridging, supporting seamless operations across diverse blockchain ecosystems.
The Rise of Prediction Markets
Decentralized prediction markets have become one of the hottest DeFi trends, especially as the US elections are just around the corner. Its popularity is so big that even mainstream platforms have cited marketplaces like Polymarket to gauge US election sentiment.
How can we explain this phenomenon? Well, prediction markets have become the go-to platforms for political and financial polling. This is due to the concept of collective intelligence, where the combined input of many people tends to result in more accurate predictions than those of individuals.
Prediction markets allow you to trade contracts based on future events. They function similarly to exchanges, where you can buy or sell shares representing possible outcomes, such as election results or sporting events. The price of these shares is determined by supply and demand, indicating the collective beliefs about the likelihood of each event. If your prediction is correct, you receive $1 per share; if not, the shares become worthless, and you lose your bet.
There are two types of prediction markets:
- Traditional Prediction Markets: These operate within regulated environments, often require identity verification (such as Know Your Customer or KYC), and may be insured by entities like the FDIC.
- Decentralized Prediction Markets: Built on blockchain, these markets offer more privacy and accessibility by removing central authority. However, they are not insured and may face regulatory restrictions in certain areas, such as the U.S.
Polymarket’s Dominance
So far, in October 2024, Polymarket controls 99% of the prediction market. The platform has recorded nearly $1B in trading volume and reached a peak of nearly 100,000 traders.
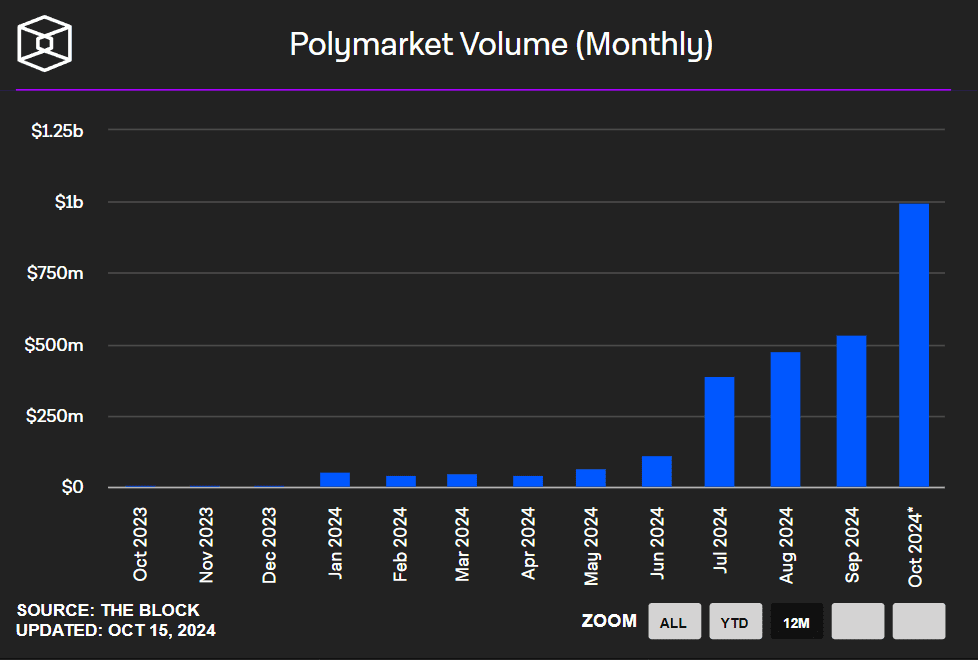
Polymarket’s main appeal is its simplicity. You can bet on a wide variety of topics, ranging from politics and entertainment to trending or even quirky events. So, you wager by buying shares that cost less than $1. If your prediction proves correct, you receive $1 per share as a reward.
Polymarket is self-custodial, meaning you control your own funds through your personal wallet. This setup gained traction during significant events, like the US elections, where users could engage in simple binary bets, predicting outcomes with “Yes” or “No” answers.
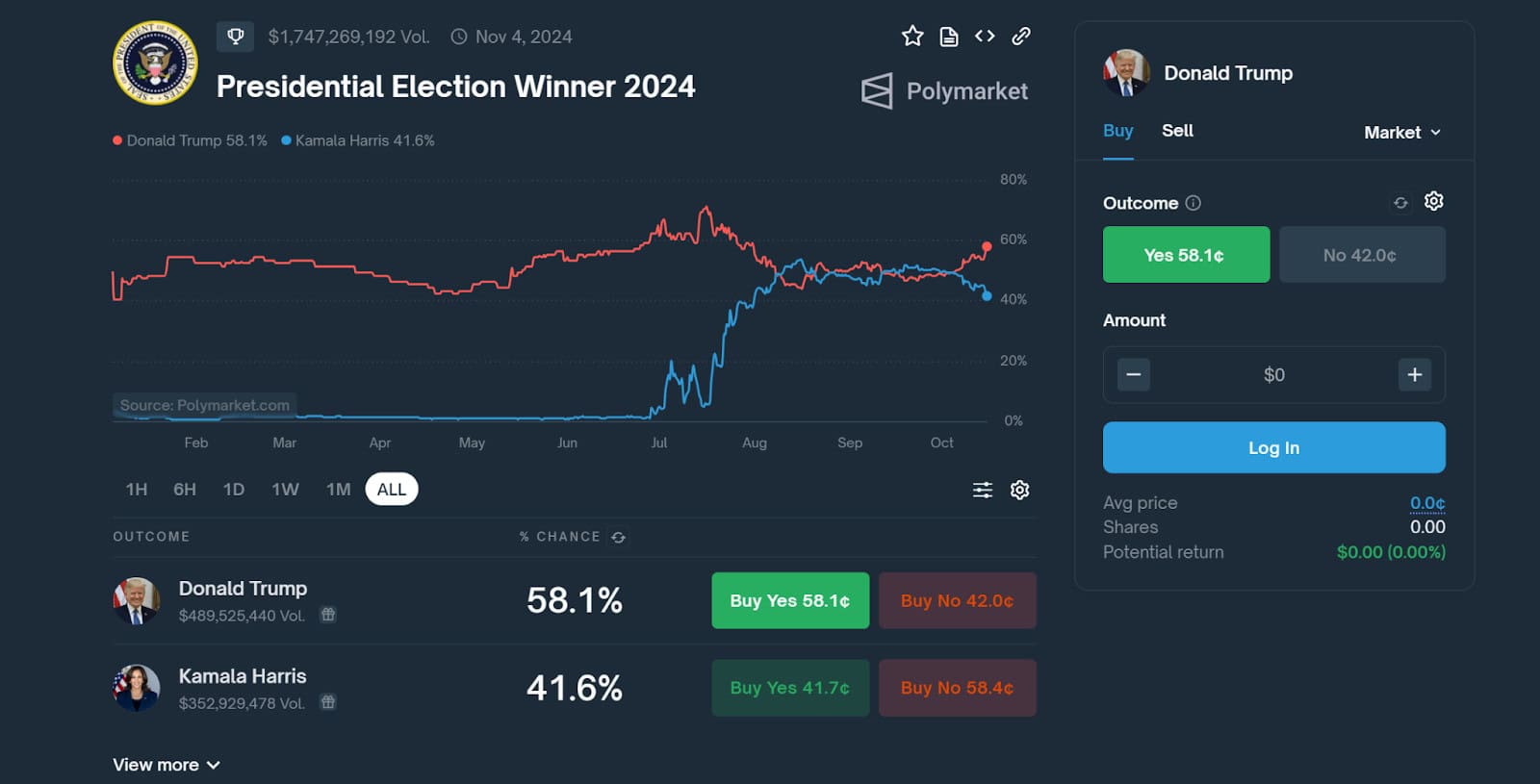
This particular market has amassed over $1B in wagered funds, the highest ever in any prediction market.
Closing Thoughts – The Top DeFi Trends in 2024
As DeFi continues to grow, new trends will continue to push the boundaries for what the DeFi sector can achieve, as well as bring new opportunities for crypto projects and traditional finance. One example of the tokenization of US treasuries becoming a $2B market, with old-school finance giants like BlackRock joining in on the fun.


